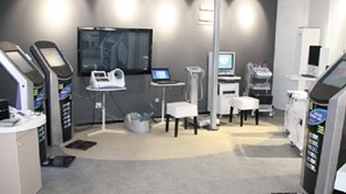
濟(jì)南易享醫(yī)療科技有限公司
濟(jì)南易享醫(yī)療科技有限公司
服務(wù)熱線:18553158035
聯(lián)系地址:濟(jì)南市高新區(qū)新濼大街1666號(hào)齊盛廣場2號(hào)樓15樓
慢病隨訪包幫助慢病人群自我監(jiān)測(cè)慢病發(fā)展
慢病隨訪包系列,專為基層慢病隨訪設(shè)計(jì)打造,滿足基層電子建檔,慢病跟蹤,數(shù)據(jù)上傳等需求
Chronic disease follow-up package series, designed and created specifically for grassroots chronic disease follow-up, to meet the needs of grassroots electronic filing, chronic disease tracking, data uploading, and more
什么是高血壓?
What is hypertension?
到醫(yī)療衛(wèi)生機(jī)構(gòu)測(cè)量血壓時(shí),非同日三次測(cè)量結(jié)果:高壓(收縮壓)都大于或等于140mmHg,或者低壓(舒張壓)都大于或等于90mmHg,就可以診斷為高血壓。如果高血壓患者在服用降壓藥物期間,雖然測(cè)得血壓值不高,仍屬于高血壓,因?yàn)檫@是在藥物控制下的血壓,一旦停了降壓藥,血壓仍會(huì)升高的。
When measuring blood pressure in medical and health institutions, if the results of three non same day measurements show that high blood pressure (systolic blood pressure) is greater than or equal to 140mmHg, or low blood pressure (diastolic blood pressure) is greater than or equal to 90mmHg, it can be diagnosed as hypertension. If a patient with hypertension is taking antihypertensive medication and their blood pressure is not high, it still belongs to hypertension because it is controlled by medication. Once the antihypertensive medication is stopped, the blood pressure will still rise.
高血壓對(duì)身體有哪些危害???患了高血壓也許沒什么癥狀,但高血壓是“無聲的殺手”,每時(shí)每刻都在損害著患者的健康。如果血壓沒有得到很好的控制,損傷到大腦,會(huì)引起腦卒中(中風(fēng))偏癱,造成半身不遂、癡呆等;損傷到心臟,會(huì)引起心絞痛、心肌梗死、心力衰竭等;損傷到眼睛,可引起眼底視網(wǎng)膜病變甚至可能導(dǎo)致失明;損傷到腎,可引起腎功能不全。
What are the hazards of hypertension to the body? Suffering from hypertension may not have many symptoms, but it is a 'silent killer' that constantly harms the health of patients. If blood pressure is not well controlled and damages the brain, it can cause stroke (hemiplegia), resulting in hemiplegia, dementia, etc; Damage to the heart can cause angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure, etc; Damage to the eyes can cause retinal lesions and even lead to blindness; Damage to the kidneys can cause renal dysfunction.
如何盡早發(fā)現(xiàn)高血壓?
How to detect hypertension as early as possible?
凡年齡在35歲以上(包括35歲)的居民,原來沒有高血壓或者不知道是否患有高血壓,每年1次到醫(yī)療機(jī)構(gòu)就診時(shí)都應(yīng)主動(dòng)接受測(cè)量血壓。也可以每年在家里至少測(cè)量1次血壓,這樣就能盡早發(fā)現(xiàn)高血壓,早期治療。當(dāng)然,初次測(cè)量血壓偏高并不能確診,還應(yīng)在去除引起血壓升高的原因(如失眠、勞累、急性疾病、焦慮等)后,再預(yù)約復(fù)查。非同日測(cè)量3次,血壓都高于正常,可初步診斷為高血壓。心電血壓工作站通過條碼掃描,能夠采集居民的血壓體溫的數(shù)據(jù),待測(cè)量完成后,能夠進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)的篩查與漏項(xiàng)提示,數(shù)據(jù)能夠?qū)崟r(shí)上傳至終端系統(tǒng),檢測(cè)效率高,檢驗(yàn)批量大。
Residents aged 35 and above (including 35 years old) who do not have hypertension or do not know if they have hypertension should actively undergo blood pressure measurement when visiting medical institutions once a year. It is also possible to measure blood pressure at home at least once a year, so that hypertension can be detected and treated early. Of course, measuring high blood pressure for the first time does not confirm a diagnosis. After removing the causes of the elevated blood pressure (such as insomnia, fatigue, acute illness, anxiety, etc.), a follow-up appointment should be scheduled. If blood pressure is higher than normal after measuring three times on different days, it can be preliminarily diagnosed as hypertension. The electrocardiogram and blood pressure workstation can collect data on residents' blood pressure and body temperature through barcode scanning. After the measurement is completed, it can screen the data and provide missing item prompts. The data can be uploaded to the terminal system in real time, with high detection efficiency and large inspection batches.
什么是糖尿病?
What is diabetes?
糖尿病是一種內(nèi)分泌代謝性疾病,是以血糖升高為特征。如果空腹時(shí)抽取靜脈血查血糖,結(jié)果大于或等于7mmoI/L,并在以后的復(fù)查中仍高于此標(biāo)準(zhǔn)者,就可以診斷為糖尿病。糖尿病可分為1型、2型和其他幾型?,其中90%以上都是2型糖尿病。2型糖尿病患者納入健康管理。如果糖尿病患者正在接受治療,有可能測(cè)得的血糖值不高,但還是糖尿病,一旦停止有效的治療,血糖還會(huì)升上去的。
Diabetes is an endocrine metabolic disease, characterized by elevated blood sugar. If venous blood is taken on an empty stomach to check blood sugar, and the result is greater than or equal to 7mmoI/L, and it is still higher than this standard in subsequent reexamination, diabetes can be diagnosed. Diabetes can be divided into type 1, type 2 and other types, of which more than 90% are type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes patients were included in health management. If a patient with diabetes is undergoing treatment, the measured blood sugar may not be high, but it is still diabetes. Once effective treatment is stopped, the blood sugar will rise.
糖尿病對(duì)人體有哪些危害?
What harm does diabetes do to the human body?
糖尿病對(duì)人體的危害主要表現(xiàn)在并發(fā)癥上。如果血糖長期得不到良好控制,能造成腦、心臟、神經(jīng)、眼和腎等重要器官的損害,甚至導(dǎo)致殘疾或死亡。糖尿病造成心、腦血管損害的患病率比非糖尿病者高3倍;因下肢血管損傷而截肢者比非糖尿病者多10倍;糖尿病腎病晚期可造成尿毒癥;糖尿病眼病造成的雙目失明者比非糖尿病都高25倍。此外,糖尿病還常伴多發(fā)性周圍神經(jīng)病變和自主神經(jīng)損害以及各種不同部位的感染。尿液分析儀可檢測(cè)尿蛋白、尿糖、尿酮體、尿潛血等10多個(gè)檢測(cè)項(xiàng)目,數(shù)據(jù)可通過藍(lán)牙、無線的方式,實(shí)時(shí)上傳至終端系統(tǒng)內(nèi),支持檢驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)報(bào)單打印,檢測(cè)輕松,操作便捷。
The harm of diabetes to human body is mainly manifested in its complications. If blood sugar is not well controlled for a long time, it can cause damage to important organs such as the brain, heart, nerves, eyes, and kidneys, and even lead to disability or death. The prevalence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular damage caused by diabetes is 3 times higher than that of non diabetes; The number of amputees due to lower limb vascular injury is 10 times more than that of non diabetes patients; Uremia can be caused by the late stage of diabetes nephropathy; The blindness caused by diabetes eye disease is 25 times higher than that caused by non diabetes eye disease. In addition, diabetes is often accompanied by multiple peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy and infection in different parts of the body. The urine analyzer can detect more than 10 detection items such as urine protein, urine sugar, urine ketone bodies, and urine occult blood. The data can be uploaded to the terminal system in real time through Bluetooth and wireless methods, and supports printing of inspection data reports, making detection easy and operation convenient.
參加糖尿病患者健康管理服務(wù)能給患者帶來哪些好處?
What benefits can participating in health management services for diabetes patients bring to patients?
糖尿病患者參加健康管理服務(wù)可以得到基層醫(yī)生主動(dòng)的、連續(xù)的服務(wù);患者會(huì)在醫(yī)生的指導(dǎo)下建立健康的生活方式,合理使用降血糖藥物,將血糖控制在理想水平,最大限度地減少糖尿病給健康帶來的危害;在管理過程,醫(yī)生會(huì)及時(shí)發(fā)現(xiàn)其他健康問題,及時(shí)調(diào)整治療方案;當(dāng)出現(xiàn)危急癥狀或存在不能處理的其他疾病時(shí),醫(yī)生會(huì)指導(dǎo)患者緊急轉(zhuǎn)診;降低患者及家屬的精神壓力,緩解因病情控制不理想而造成的經(jīng)濟(jì)壓力。
Diabetes patients participating in health management services can receive active and continuous services from grass-roots doctors; Patients will establish a healthy lifestyle under the guidance of doctors, use hypoglycemic drugs reasonably, control blood sugar at an ideal level, and minimize the harm of diabetes to health; During the management process, doctors will promptly identify other health issues and adjust treatment plans accordingly; When there are critical symptoms or other illnesses that cannot be treated, doctors will guide patients to emergency referrals; Reduce the mental stress of patients and their families, and alleviate the economic pressure caused by poor disease control.
如何盡早發(fā)現(xiàn)糖尿病?糖尿病的典型癥狀是我們常說的“三多一少”,即多飲、多食、多尿、體重減輕。但不是所有的糖尿病患者都有“三多一少”的典型癥狀。如果出現(xiàn)些可疑癥狀,如:皮膚瘙癢、饑餓感、視物不清、經(jīng)常感到疲乏、勞累或反復(fù)感染等時(shí),尤其有糖尿病家族史、生活壓力大、多食、肥胖、缺乏體力活動(dòng)者,患病的可能性更大。建議每年去醫(yī)院檢查血糖,確診或排除糖尿病。
How to find diabetes as soon as possible? The typical symptom of diabetes is what we often call "more than three and less", that is, drinking more, eating more, urinating more and losing weight. But not all patients with diabetes have the typical symptoms of "more than three and less". If there are some suspicious symptoms, such as skin itching, hunger, blurred vision, often feeling tired, tired or repeatedly infected, especially those with diabetes family history, high life pressure, overeating, obesity, and lack of physical activity, they are more likely to get sick. It is recommended to go to the hospital to check blood sugar every year to diagnose or eliminate diabetes.
高血壓、糖尿病篩查方法是什么?
What is the screening method for hypertension and diabetes?
高血壓的篩查:
Screening for hypertension:
1.對(duì)轄區(qū)內(nèi)35歲及以上常住居民,每年為其免費(fèi)測(cè)量一次血壓(非同日三次測(cè)量)。2.對(duì)第一次發(fā)現(xiàn)收縮壓≥140mmHg和(或)舒張壓≥90mmHg的居民在去除可能引起血壓升高的因素后預(yù)約其復(fù)查,非同日3次測(cè)量血壓均高于正常,可初步診斷為高血壓。
1. For permanent residents aged 35 and above within the jurisdiction, their blood pressure will be measured free of charge once a year (not three times on the same day). 2. For residents whose systolic blood pressure is ≥ 140mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure is ≥ 90mmHg for the first time, after removing factors that may cause blood pressure elevation, make an appointment for follow-up. If the blood pressure is higher than normal on three non same day measurements, it can be preliminarily diagnosed as hypertension.
糖尿病的篩查:對(duì)2型糖尿病高危人群進(jìn)行有針對(duì)性的健康教育,建議其每年至少測(cè)量1次空腹血糖,并接受醫(yī)務(wù)人員的健康指導(dǎo)。點(diǎn)擊圖片查看更多詳細(xì)信息
Screening of diabetes: targeted health education should be carried out for people at high risk of type 2 diabetes. It is recommended that they measure fasting blood glucose at least once a year and receive health guidance from medical personnel. Click on the image to view more detailed information
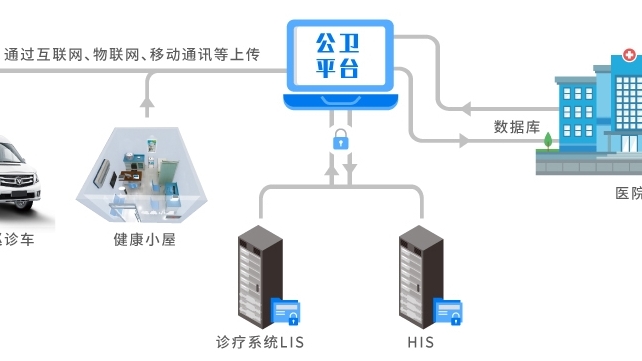
國家基本公共衛(wèi)生智能查體采集設(shè)備及系統(tǒng),依據(jù)《國家基本公共衛(wèi)生服務(wù)規(guī)范》的要求,協(xié)助基層醫(yī)生對(duì)轄區(qū)內(nèi)居民進(jìn)行健康體檢及慢病隨訪等健康管理的工作,針對(duì)各類鄉(xiāng)鎮(zhèn)衛(wèi)生院公衛(wèi)體檢設(shè)計(jì)打造。
The national basic public health intelligent physical examination collection equipment and system, in accordance with the requirements of the National Basic Public Health Service Standards, assist grassroots doctors in conducting health examinations and chronic disease follow-up for residents in their jurisdiction, and design and build public health examinations for various township health centers.
為什么要對(duì)慢性病患者提供健康管理服務(wù)???當(dāng)前慢性病已經(jīng)成為了危害我國人民群眾身體健康的一個(gè)重大公共衛(wèi)生問題。高血壓、糖尿病是可以預(yù)防和控制的,關(guān)鍵是提高大眾的知曉率、治療率和控制率,在醫(yī)生的建議下學(xué)會(huì)自我監(jiān)測(cè),逐步改善不良生活方式及按醫(yī)囑合理使用藥物,從而將病情控制在理想水平,減少并發(fā)癥的發(fā)生與發(fā)展,就可以避免巨大的疾病痛苦,同時(shí)減輕家庭、國家的沉重經(jīng)濟(jì)負(fù)擔(dān)。
Why provide health management services for chronic disease patients? Chronic diseases have become a major public health issue that poses a threat to the physical health of the Chinese people. Hypertension and diabetes can be prevented and controlled. The key is to improve the awareness rate, treatment rate and control rate of the public, learn self-monitoring under the doctor's advice, gradually improve the bad lifestyle and use drugs reasonably according to the doctor's advice, so as to control the condition at an ideal level and reduce the occurrence and development of complications, which can avoid huge disease pain and reduce the heavy economic burden of families and the country.
慢性病患者健康管理服務(wù)包括哪些內(nèi)容?
What are the contents of health management services for chronic disease patients?
篩查:主要是發(fā)現(xiàn)高血壓、糖尿病患者和具有高血壓、糖尿病高危因素的易感人群。隨訪評(píng)估:每年至少4次的面對(duì)面隨訪,首先測(cè)量血壓、血糖,如無危急情況,常規(guī)隨訪內(nèi)容還包括詢問、檢查與病情評(píng)估。隨訪評(píng)估內(nèi)容包括①測(cè)量血壓、血糖并評(píng)估是否存在危急情況,如果血壓、血糖很高,或有危急癥狀,或存在不能處理的其他疾病時(shí),需要緊急轉(zhuǎn)診。②對(duì)不需緊急轉(zhuǎn)診的患者,要詢問上次隨訪至此次隨訪期間的癥狀。③測(cè)量心率、體重,判斷是否超重或肥胖,糖尿病患者還需要檢查足背動(dòng)脈搏動(dòng)。④詢問患者疾病情況以及生活方式,了解患者服藥情況。⑤做針對(duì)性健康教育,與患者一起制定生活方式改進(jìn)目標(biāo),并告訴患者出現(xiàn)哪些異常時(shí)應(yīng)立即就診。分類干預(yù):醫(yī)生根據(jù)血壓/血糖控制情況、用藥有無不良反應(yīng)及并發(fā)癥情況,對(duì)不同患者進(jìn)行有針對(duì)性的干預(yù)處理并進(jìn)行健康指導(dǎo)。健康體檢:每年1次比較全面的健康體檢和針對(duì)性健康指導(dǎo)。健康體檢內(nèi)容包括健康體檢內(nèi)容包括體溫、脈搏、呼吸、血壓、身高、體重、腰圍、皮膚、淺表淋巴結(jié)、心臟、肺部、腹部等常規(guī)體格檢查。
Screening: mainly to find patients with hypertension, diabetes and susceptible groups with high risk factors of hypertension and diabetes. Follow up evaluation: At least 4 face-to-face visits per year, blood pressure and blood sugar are measured first. If there are no critical situations, routine follow-up content also includes inquiries, examinations, and disease assessments. The follow-up assessment includes measuring blood pressure and blood sugar and evaluating whether there is a critical situation. If blood pressure and blood sugar are high, or there are critical symptoms, or other diseases that cannot be treated, emergency referral is needed. ② For patients who do not require emergency referral, inquire about their symptoms from the last follow-up to this follow-up. ③ To measure heart rate and body weight and judge whether overweight or obesity, patients with diabetes also need to check the pulse of the dorsalis pedis artery. ④ Inquire about the patient's illness and lifestyle, and understand their medication status. ⑤ Provide targeted health education, work with patients to set lifestyle improvement goals, and inform them of any abnormalities that require immediate medical attention. Classification intervention: Doctors provide targeted intervention and health guidance to different patients based on their blood pressure/blood sugar control, medication adverse reactions, and complications. Health check-up: A comprehensive health check-up and targeted health guidance once a year. The health examination includes routine physical examinations such as body temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, height, weight, waist circumference, skin, superficial lymph nodes, heart, lungs, abdomen, etc.
慢性病患者應(yīng)怎樣配合做好健康管理工作???國家免費(fèi)為慢性病患者提供健康管理服務(wù),延緩疾病發(fā)展,控制并發(fā)癥,提高患者生活質(zhì)量,患者及家屬應(yīng)認(rèn)真配合做好該項(xiàng)工作。1、納入慢性病健康管理:高血壓、糖尿病患者明確診斷后,應(yīng)盡快主動(dòng)到常住地鄉(xiāng)鎮(zhèn)衛(wèi)生院、村衛(wèi)生室或社區(qū)衛(wèi)生服務(wù)中心(站)建立健康檔案,固定責(zé)任醫(yī)生,接受健康管理。2、按時(shí)隨訪體檢:按照醫(yī)生通知的預(yù)約時(shí)間、地點(diǎn),接受隨訪和健康體檢服務(wù)。3、遵醫(yī)服藥:隨訪和體檢時(shí),應(yīng)向醫(yī)生如實(shí)告知病情與治療情況,嚴(yán)格按照醫(yī)囑按時(shí)按量服藥,嚴(yán)禁擅自停藥、減量或換藥,以免發(fā)生意外(服藥過程中感到不適或發(fā)生不良反應(yīng)時(shí),應(yīng)及時(shí)聯(lián)系醫(yī)生調(diào)整治療方案)。4、接受生活方式指導(dǎo):非藥物治療是高血壓、糖尿病治療中十分重要的內(nèi)容,包括戒煙、限酒、減鹽、減重等多個(gè)方面,患者應(yīng)與醫(yī)生共同制定相應(yīng)的控制目標(biāo)和具體的達(dá)標(biāo)方法。? ??5、及時(shí)轉(zhuǎn)診:遇到危急情況或者血壓持續(xù)控制不滿意時(shí),應(yīng)聽從醫(yī)生建議,及時(shí) 轉(zhuǎn)診到大醫(yī)院。
How should chronic disease patients cooperate to do a good job in health management? The state provides free health management services for chronic disease patients, delaying disease progression, controlling complications, and improving patients' quality of life. Patients and their families should cooperate seriously in this work. 1. Incorporated into chronic disease health management: After the hypertension and diabetes patients have been diagnosed clearly, they should actively go to the township hospitals, village clinics or community health service centers (stations) in their permanent residence as soon as possible to establish health records, fix the responsible doctors, and accept health management. 2. Follow up physical examination on time: Accept follow-up and health examination services according to the appointment time and location notified by the doctor. 3. Follow up and take medication: During follow-up and physical examinations, truthfully inform the doctor of the condition and treatment situation, strictly follow the doctor's advice to take medication on time and in the prescribed amount, and strictly prohibit unauthorized stopping, reducing or changing of medication to avoid accidents (if discomfort or adverse reactions occur during medication, timely contact the doctor to adjust the treatment plan). 4. Lifestyle guidance: Non drug treatment is a very important content in the treatment of hypertension and diabetes, including smoking cessation, alcohol restriction, salt reduction, weight loss and other aspects. Patients should work with doctors to develop corresponding control goals and specific methods to achieve goals. 5. Timely referral: In case of critical situations or unsatisfactory blood pressure control, follow the doctor's advice and promptly refer to a large hospital.
本文由 慢病隨訪包 友情奉獻(xiàn).更多有關(guān)的知識(shí)請(qǐng)點(diǎn)擊 http://www.rcforging.com/ 真誠的態(tài)度.為您提供為全面的服務(wù).更多有關(guān)的知識(shí)我們將會(huì)陸續(xù)向大家奉獻(xiàn).敬請(qǐng)期待.
This article is contributed by the Chronic Disease Follow up Package For more related knowledge, please click http://www.rcforging.com/ Sincere attitude To provide you with comprehensive services We will gradually contribute more relevant knowledge to everyone Coming soon.
相關(guān)文章 / Recommended news
- 一般來說公衛(wèi)隨訪箱有哪些必要的醫(yī)療設(shè)備?
- 慢病隨訪包幫助慢病人群自我監(jiān)測(cè)慢病發(fā)展
- 公衛(wèi)隨訪包助力基本公共衛(wèi)生項(xiàng)目順利落地
- 公共衛(wèi)生慢病隨訪包,打通慢病管理最初百米
- 哪些場合需要用到健康一體機(jī)?健康體檢一體機(jī)應(yīng)用場景介紹!
- 醫(yī)養(yǎng)體檢包的 發(fā)展前景是怎樣的?
- 什么人群適合常備醫(yī)養(yǎng)體檢包?
- 公衛(wèi)隨訪包:智慧隨訪設(shè)備,賦能基層醫(yī)療
- 慢病隨訪包:激發(fā)縣域慢病管理運(yùn)營效率
- 公共衛(wèi)生服務(wù)慢病隨訪,“隨訪一體機(jī)”成基層醫(yī)生的“掌中寶”